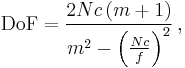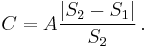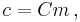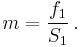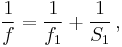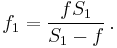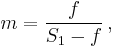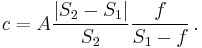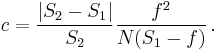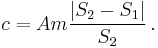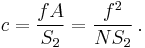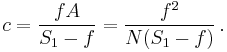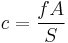Circle of confusion
In optics, a circle of confusion is an optical spot caused by a cone of light rays from a lens not coming to a perfect focus when imaging a point source. It is also known as disk of confusion, circle of indistinctness, blur circle, or blur spot.
In photography, the circle of confusion (“CoC”) is used to determine the depth of field, the part of an image that is acceptably sharp. A standard value of CoC is often associated with each image format, but the most appropriate value depends on visual acuity, viewing conditions, and the amount of enlargement. Properly, this is the maximum permissible circle of confusion, the circle of confusion diameter limit, or the circle of confusion criterion, but is often informally called simply the circle of confusion.
Real lenses do not focus all rays perfectly, so that even at best focus, a point is imaged as a spot rather than a point. The smallest such spot that a lens can produce is often referred to as the circle of least confusion.
Contents |
Two uses
Two important uses of this term and concept need to be distinguished:
- For describing the largest blur spot that is indistinguishable from a point. A lens can precisely focus objects at only one distance; objects at other distances are defocused. Defocused object points are imaged as blur spots rather than points; the greater the distance an object is from the plane of focus, the greater the size of the blur spot. Such a blur spot has the same shape as the lens aperture, but for simplicity, is usually treated as if it were circular. In practice, objects at considerably different distances from the camera can still appear sharp (Ray 2000, 50); the range of object distances over which objects appear sharp is the depth of field (“DoF”). The common criterion for “acceptable sharpness” in the final image (e.g., print, projection screen, or electronic display) is that the blur spot be indistinguishable from a point.
- For describing the blur spot achieved at a lens’s best focus. Recognizing that real lenses do not focus all rays perfectly under even the best conditions, the circle of confusion of a lens is a characterization of that blur spot. The term circle of least confusion is often used for the smallest blur spot a lens can make (Ray 2002, 89), for example by picking a best focus position that makes a good compromise between the varying effective focal lengths of different lens zones due to spherical or other aberrations. Diffraction effects from wave optics and the finite aperture of a lens can be included in the circle of least confusion, or the term can be applied in pure ray (geometric) optics.
In idealized ray optics, where rays are assumed to converge to a point when perfectly focused, the shape of a defocus blur spot from a lens with a circular aperture is a hard-edged circle of light. A more general blur spot has soft edges due to diffraction and aberrations (Stokseth 1969, 1317; Merklinger 1992, 45–46), and may be non-circular due to the aperture shape. So the diameter concept needs to be carefully defined to be meaningful. Suitable definitions often use the concept of encircled energy, the fraction of the total optical energy of the spot that is within the specified diameter. Values of the fraction (e.g., 80%, 90%) vary with application.
Circle of confusion diameter limit in photography
In photography, the circle of confusion diameter limit (“CoC”) for the final image is often defined as the largest blur spot that will still be perceived by the human eye as a point.
With this definition, the CoC in the original image (the image on the film or electronic sensor) depends on three factors:
- Visual acuity. For most people, the closest comfortable viewing distance, termed the near distance for distinct vision (Ray 2000, 52), is approximately 25 cm. At this distance, a person with good vision can usually distinguish an image resolution of 5 line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm), equivalent to a CoC of 0.2 mm in the final image.
- Viewing conditions. If the final image is viewed at approximately 25 cm, a final-image CoC of 0.2 mm often is appropriate. A comfortable viewing distance is also one at which the angle of view is approximately 60° (Ray 2000, 52); at a distance of 25 cm, this corresponds to about 30 cm, approximately the diagonal of an 8″×10″ image. It often may be reasonable to assume that, for whole-image viewing, a final image larger than 8″×10″ will be viewed at a distance correspondingly greater than 25 cm, and for which a larger CoC may be acceptable; the original-image CoC is then the same as that determined from the standard final-image size and viewing distance. But if the larger final image will be viewed at the normal distance of 25 cm, a smaller original-image CoC will be needed to provide acceptable sharpness.
- Enlargement from the original image to the final image. If there is no enlargement (e.g., a contact print of an 8×10 original image), the CoC for the original image is the same as that in the final image. But if, for example, the long dimension of a 35 mm original image is enlarged to 25 cm (10 inches), the enlargement is approximately 7×, and the CoC for the original image is 0.2 mm / 7, or 0.029 mm.
The common values for CoC may not be applicable if reproduction or viewing conditions differ significantly from those assumed in determining those values. If the original image will be given greater enlargement, or viewed at a closer distance, then a smaller CoC will be required. All three factors above are accommodated with this formula:
- CoC (mm) = viewing distance (cm) / desired final-image resolution (lp/mm) for a 25 cm viewing distance / enlargement / 25
For example, to support a final-image resolution equivalent to 5 lp/mm for a 25 cm viewing distance when the anticipated viewing distance is 50 cm and the anticipated enlargement is 8:
- CoC = 50 / 5 / 8 / 25 = 0.05 mm
Since the final-image size is not usually known at the time of taking a photograph, it is common to assume a standard size such as 25 cm width, along with a conventional final-image CoC of 0.2 mm, which is 1/1250 of the image width. Conventions in terms of the diagonal measure are also commonly used. The DoF computed using these conventions will need to be adjusted if the original image is cropped before enlarging to the final image size, or if the size and viewing assumptions are altered.
Using the “Zeiss formula”, the circle of confusion is sometimes calculated as d/1730 where d is the diagonal measure of the original image (the camera format). For full-frame 35 mm format (24 mm × 36 mm, 43 mm diagonal) this comes out to be 0.024 mm. A more widely used CoC is d/1500, or 0.029 mm for full-frame 35 mm format, which corresponds to resolving 5 lines per millimeter on a print of 30 cm diagonal. Values of 0.030 mm and 0.033 mm are also common for full-frame 35 mm format. For practical purposes, d/1730, a final-image CoC of 0.2 mm, and d/1500 give very similar results.
Criteria relating CoC to the lens focal length have also been used. Kodak (1972, 5) recommended 2 minutes of arc (the Snellen criterion of 30 cycles/degree for normal vision) for critical viewing, giving CoC ≈ f /1720, where f is the lens focal length. For a 50 mm lens on full-frame 35 mm format, this gave CoC ≈ 0.0291 mm. This criterion evidently assumed that a final image would be viewed at “perspective-correct” distance (i.e., the angle of view would be the same as that of the original image):
- Viewing distance = focal length of taking lens × enlargement
However, images seldom are viewed at the “correct” distance; the viewer usually doesn't know the focal length of the taking lens, and the “correct” distance may be uncomfortably short or long. Consequently, criteria based on lens focal length have generally given way to criteria (such as d/1500) related to the camera format.
If an image is viewed on a low-resolution display medium such as a computer monitor, the detectability of blur will be limited by the display medium rather than by human vision. For example, the optical blur will be more difficult to detect in an 8″×10″ image displayed on a computer monitor than in an 8″×10″ print of the same original image viewed at the same distance. If the image is to be viewed only on a low-resolution device, a larger CoC may be appropriate; however, if the image may also be viewed in a high-resolution medium such as a print, the criteria discussed above will govern.
Depth of field formulas derived from geometrical optics imply that any arbitrary DoF can be achieved by using a sufficiently small CoC. Because of diffraction, however, this isn't quite true. Using a smaller CoC requires increasing the lens f-number to achieve the same DOF, and if the lens is stopped down sufficiently far, the reduction in defocus blur is offset by the increased blur from diffraction. See the Depth of field article for a more detailed discussion.
Circle of confusion diameter limit based on d/1500
| Image Format | Frame size[1] | CoC |
|---|---|---|
| Small Format | ||
| Nikon 1 series | 8.8 mm × 13.2 mm | 0.011 mm |
| Four Thirds System | 13.5 mm × 18 mm | 0.015 mm |
| APS-C[2] | 15.0 mm × 22.5 mm | 0.018 mm |
| APS-C Canon | 14.8 mm × 22.2 mm | 0.018 mm |
| APS-C Nikon/Pentax/Sony | 15.7 mm × 23.6 mm | 0.019 mm |
| APS-H Canon | 19.0 mm × 28.7 mm | 0.023 mm |
| 35 mm | 24 mm × 36 mm | 0.029 mm |
| Medium Format | ||
| 645 (6×4.5) | 56 mm × 42 mm | 0.047 mm |
| 6×6 | 56 mm × 56 mm | 0.053 mm |
| 6×7 | 56 mm × 69 mm | 0.059 mm |
| 6×9 | 56 mm × 84 mm | 0.067 mm |
| 6×12 | 56 mm × 112 mm | 0.083 mm |
| 6×17 | 56 mm × 168 mm | 0.12 mm |
| Large Format | ||
| 4×5 | 102 mm × 127 mm | 0.11 mm |
| 5×7 | 127 mm × 178 mm | 0.15 mm |
| 8×10 | 203 mm × 254 mm | 0.22 mm |
Adjusting the circle of confusion diameter for a lens’s DoF scale
The f-number determined from a lens DoF scale can be adjusted to reflect a CoC different from the one on which the DoF scale is based. It is shown in the Depth of field article that
where N is the lens f-number, c is the CoC, m is the magnification, and f is the lens focal length. Because the f-number and CoC occur only as the product Nc, an increase in one is equivalent to a corresponding decrease in the other, and vice versa. For example, if it is known that a lens DoF scale is based on a CoC of 0.035 mm, and the actual conditions require a CoC of 0.025 mm, the CoC must be decreased by a factor of 0.035 / 0.025 = 1.4; this can be accomplished by increasing the f-number determined from the DoF scale by the same factor, or about 1 stop, so the lens can simply be closed down 1 stop from the value indicated on the scale.
The same approach can usually be used with a DoF calculator on a view camera.
Determining a circle of confusion diameter from the object field
To calculate the diameter of the circle of confusion in the image plane for an out-of-focus subject, one method is to first calculate the diameter of the blur circle in a virtual image in the object plane, which is simply done using similar triangles, and then multiply by the magnification of the system, which is calculated with the help of the lens equation.
The blur circle, of diameter C, in the focused object plane at distance S1, is an unfocused virtual image of the object at distance S2 as shown in the diagram. It depends only on these distances and the aperture diameter A, via similar triangles, independent of the lens focal length:
The circle of confusion in the image plane is obtained by multiplying by magnification m:
where the magnification m is given by the ratio of focus distances:
Using the lens equation we can solve for the auxiliary variable f1:
which yields
and express the magnification in terms of focused distance and focal length:
which gives the final result:
This can optionally be expressed in terms of the f-number N = f/A as:
This formula is exact for a simple paraxial thin lens or a symmetrical lens, in which the entrance pupil and exit pupil are both of diameter A. More complex lens designs with a non-unity pupil magnification will need a more complex analysis, as addressed in depth of field.
More generally, this approach leads to an exact paraxial result for all optical systems if A is the entrance pupil diameter, the subject distances are measured from the entrance pupil, and the magnification is known:
If either the focus distance or the out-of-focus subject distance is infinite, the equations can be evaluated in the limit. For infinite focus distance:
And for the blur circle of an object at infinity when the focus distance is finite:
If the c value is fixed as a circle of confusion diameter limit, either of these can be solved for subject distance to get the hyperfocal distance, with approximately equivalent results.
History
Henry Coddington 1829
Before it was applied to photography, the concept of circle of confusion was applied to optical instruments such as telescopes. Coddington (1829, 54) quantifies both a circle of least confusion and a least circle of confusion for a spherical reflecting surface.
- "This we may consider as the nearest approach to a simple focus, and term the circle of least confusion."
Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge 1832
The Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (1832, 11) applied it to third-order aberrations:
- "This spherical aberration produces an indistinctness of vision, by spreading out every mathematical point of the object into a small spot in its picture; which spots, by mixing with each other, confuse the whole. The diameter of this circle of confusion, at the focus of the central rays F, over which every point is spread, will be L K (fig. 17.); and when the aperture of the reflector is moderate it equals the cube of the aperture, divided by the square of the radius (...): this circle is called the aberration of latitude."
T.H. 1866
Circle-of-confusion calculations: An early precursor to depth of field calculations is the T.H. (1866, 138) calculation of a circle-of-confusion diameter from a subject distance, for a lens focused at infinity; this article was pointed out by von Rohr (1899). The formula he comes up with for what he terms "the indistinctness" is equivalent, in modern terms, to
for focal length  , aperture diameter A, and subject distance S. But he does not invert this to find the S corresponding to a given c criterion (i.e. he does not solve for the hyperfocal distance), nor does he consider focusing at any other distance than infinity.
, aperture diameter A, and subject distance S. But he does not invert this to find the S corresponding to a given c criterion (i.e. he does not solve for the hyperfocal distance), nor does he consider focusing at any other distance than infinity.
He finally observes "long-focus lenses have usually a larger aperture than short ones, and on this account have less depth of focus" [his italic emphasis].
Dallmeyer and Abney
T Dallmeyer (1892, 24), in an expanded re-publication of his father John Henry Dallmeyer's 1874 pamphlet On the Choice and Use of Photographic Lenses (in material that is not in the 1874 edition and appears to have been added from a paper by J.H.D. "On the Use of Diaphragms or Stops" of unknown date) says:
- "Thus every point in an object out of focus is represented in the picture by a disc, or circle of confusion, the size of which is proportionate to the aperture in relation to the focus of the lens employed. If a point in the object is 1/100 of an inch out of focus, it will be represented by a circle of confusion measuring but 1/100 part of the aperture of the lens."
This latter statement is clearly incorrect, or misstated, being off by a factor of focal distance (focal length). He goes on:
- "and when the circles of confusion are sufficiently small the eye fails to see them as such; they are then seen as points only, and the picture appears sharp. At the ordinary distance of vision, of from twelve to fifteen inches, circles of confusion are seen as points, if the angle subtended by them does not exceed one minute of arc, or roughly, if they do not exceed the 1/100 of an inch in diameter."
Numerically, 1/100 of an inch at 12 to 15 inches is closer to two minutes of arc. This choice of COC limit remains (for a large print) the most widely used even today. Abney (1881, 207–08) takes a similar approach based on a visual acuity of one minute of arc, and chooses a circle of confusion of 0.025 cm for viewing at 40 to 50 cm, essentially making the same factor-of-two error in metric units. It is unclear whether Abney or Dallmeyer was earlier to set the COC standard thereby.
Wall 1889
The common 1/100 inch COC limit has been applied to blur other than defocus blur. For example, Wall (1889, 92) says:
- "To find how quickly a shutter must act to take an object in motion that there may be a circle of confusion less than 1/100in. in diameter, divide the distance of the object by 100 times the focus of the lens, and divide the rapidity of motion of object in inches per second by the results, when you have the longest duration of exposure in fraction of a second."
See also
Notes
- ^ The frame size is an average of cameras that take photographs of this format. For example, not all 6×7 cameras take frames that are exactly 56 mm × 69 mm. Check with the specifications of a particular camera if this level of exactness is needed.
- ^ “APS-C” is a common format for digital SLRs. Dimensions vary slightly among different manufacturers; for example, Canon’s APS-C format is nominally 15.0 mm × 22.5 mm, while Nikon’s DX format is nominally 16 mm × 24 mm. Exact dimensions sometimes vary slightly among models with the same nominal format from a given manufacturer.
References
- Abney, Sir William de Wiveleslie. 1881. A Treatise on Photography. London: Longmans, Green and Co.
- Coddington, Henry. 1829. A Treatise on the Reflexion and Refraction of light: being Part I. of a System of Optics. Cambridge: J. Smith.
- Dallmeyer, John Henry. 1874. On the Choice and Use of Photographic Lenses. New York: E. and H.T. Anthony and Co.
- Dallmeyer, Thomas R. 1892. On the Choice and Use of Photographic Lenses. London: J. Pitcher.
- Eastman Kodak Company. 1972. Optical Formulas and Their Application, Kodak Publication No. AA-26, Rev. 11-72-BX. Rochester, New York: Eastman Kodak Company.
- Kodak. See Eastman Kodak Company.
- Merklinger, Harold M. 1992. The INs and OUTs of FOCUS: An Alternative Way to Estimate Depth-of-Field and Sharpness in the Photographic Image. v. 1.0.3. Bedford, Nova Scotia: Seaboard Printing Limited. ISBN 0-9695025-0-8. Version 1.03e available in PDF at http://www.trenholm.org/hmmerk/.
- Ray, Sidney F. 2000. The geometry of image formation. In The Manual of Photography: Photographic and Digital Imaging, 9th ed. Ed. Ralph E. Jacobson, Sidney F. Ray, Geoffrey G. Atteridge, and Norman R. Axford. Oxford: Focal Press. ISBN 0-240-51574-9
- Ray, Sidney F. 2002. Applied Photographic Optics, 3rd ed. Oxford: Focal Press. ISBN 0-240-51540-4
- Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge. 1832. Natural Philosophy: With an Explanation of Scientific Terms, and an Index. London: Baldwin and Cradock, Paternoster-Row.
- Stokseth, Per A. 1969. Properties of a Defocused Optical System. Journal of the Optical Society of America 59:10, Oct. 1969.
- T.H. [pseud.]. 1866. “Long and Short Focus”. British Journal of Photography 13.
- von Rohr, Moritz. 1899. Photographische Objektiv. Berlin: Verlag Julius Springer.
- Wall, Edward John. 1889. A Dictionary of Photography for the Amateur and Professional Photographer. New York: E. and H.T. Anthony and Co.
External links
- Circles of Confusion for Digital Cameras DOFMaster
- Depth of field and circle of confusion
- Depth of Field in Depth (PDF) Includes discussion of circle of confusion criteria
- What Is the “Circle of Confusion” ƒ/Calc